HTML Images
- Images can improve the design and the appearance of a web page.
- Images are not technically inserted into a web page; images are linked to web pages. The
<img>tag creates a holding space for the referenced image. - The
<img>tag is empty; it contains attributes only and does not have a closing tag.
The <img> tag has two required attributes:
- src - Specifies the path to the image.
- alt - Specifies an alternate text for the image (for slow connections, errors in the src attribute, or screen readers).
There are two ways to specify the URL in the src attribute:
- Absolute URL - Links to an external image hosted on another website. Example:
src="https://www.w3schools.com/images/img_girl.jpg". - Relative URL - Links to an image hosted within the website. If the URL begins without a slash, it is relative to the current page. Example:
src="img_girl.jpg". If the URL begins with a slash, it is relative to the domain. Example:src="/images/img_girl.jpg". It's often best to use relative URLs to avoid breaking links when changing the domain.
Syntax:
<img src="url" alt="alternatetext">
Example 1:

OUTPUT:
Example 2:
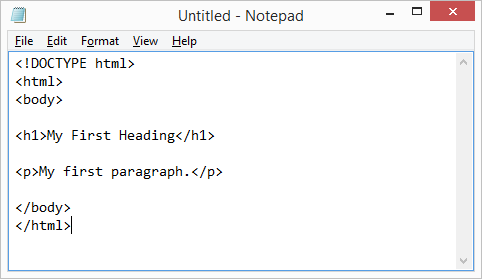
OUTPUT:
Height and Width Attributes:
The <img> tag should also contain the width and height attributes, which specify the width and height of the image.
Image as Link:
To use an image as a link, put the <img> tag inside the <a> tag.
Example:

OUTPUT:
Some Image Formats:
| Abbreviation | File Format | File Extension |
|---|---|---|
| APNG | Animated Portable Network Graphics | .apng |
| GIF | Graphics Interchange Format | .gif |
| ICO | Microsoft Icon | .ico, .cur |
| JPEG | Joint Photographic Expert Group image | .jpg, .jpeg, .jfif, .pjpeg, .pjp |
| PNG | Portable Network Graphics | .png |
| SVG | Scalable Vector Graphics | .svg |